如何在 Python 中解析 JSON
已發表: 2022-02-09JSON是一種流行的數據交換格式。 Python 附帶一個內置的JSON模塊來解析和處理 JSON 數據。 本教程將教您如何在 Python 中使用 JSON。
在本教程結束時,您將學會:
- JSON的基礎知識,
- 如何在 Python 中解析和創建 JSON 字符串,以及
- 如何在 Python 中讀取和寫入 JSON 文件。
開始吧!
什麼是 JSON?
JSON代表Java S cript Object Notation ,它是一種基於文本的數據交換格式。 儘管 JSON 最初是受到 JavaScript 對象的啟發,但幾乎所有的編程語言都支持使用 JSON。
如果您曾經使用過 API 或通讀過配置文件,您可能會遇到 JSON。
查詢 API 時以 JSON 格式發送和接收數據。 JSON 也廣泛用於軟件應用程序中的客戶端-服務器通信。 此外,您還可以將 JSON 用於通用數據存儲。
JSON 的格式與 Python 字典的格式非常相似。 字典是 Python 中強大的內置數據結構,可將數據存儲在鍵值對中。
在我們進一步討論之前,這裡有幾點值得注意:
- 在 Python 中,JSON 對象存儲為字典。
- JSON 中的數組存儲為 Python 列表。
- 在 JSON 中,布爾值表示為
true和false。 在 Python 中,這些被轉換為布爾值True和False。
有關從 JSON 轉換為 Python 的數據類型的更多詳細信息,請閱讀此處的文檔。
由於json模塊是 Python 標準庫的一部分,因此您不必安裝它。 您可以導入到當前目錄,如下所示:
import json如何在 Python 中加載 JSON 字符串
在 Python 中加載 JSON 字符串的一般語法是:
<dict_obj> = json.loads(<json_str>)這裡,
-
<dict_obj>是您要加載 JSON 字符串的 Python 字典, -
<json_str>是任何有效的 JSON 字符串。
這會將<json_str>加載到 Python 字典<dict_obj>中。
讓我們編寫一個示例。 這裡json_str是一個 JSON 字符串。
json_str = ''' { "books": [ { "title": "The Wind in the Willows", "author": "Kenneth Grahame", "year": "1908" }, { "title": "To the Lighthouse", "author": "Virginia Woolf", "year": "1927" } ] } ''' 下面的代碼片段展示瞭如何使用loads()方法將 JSON 字符串json_str加載到 Python 字典中。 您可以使用內置的type()函數來驗證py_dict是 Python 字典。
py_dict = json.loads(json_str) type(py_dict) # Output: dict print(py_dict) # Output {'books': [{'title': 'The Wind in the Willows', 'author': 'Kenneth Grahame', 'year': '1908'}, {'title': 'To the Lighthouse', 'author': 'Virginia Woolf', 'year': '1927'}]} 如上代碼所示,JSON 字符串中的所有字段都是py_dict中的鍵值對。
如何在 Python 中創建 JSON 字符串
假設您有一本 Python 字典。 那麼如何從它創建一個 JSON 字符串呢?
您可以使用具有以下語法的dumps()方法來執行此操作:
<json_str> = json.dumps(<dict_obj>)這裡,
-
<dict_obj>是您要從中創建 JSON 字符串的 Python 字典, -
<json_str>是生成的 JSON 字符串。
因此 dumps dumps()方法將<dict_obj>轉儲到 JSON 字符串<json_str>中。
到我們現有的 Python 字典py_dict 。 讓我們添加一個新鍵"movies" 。 您可以按照以下代碼片段所示進行操作:
py_dict["movies"] = [{"title":"The Imitation Game","year":"2014", "lang":"en","watched":True}] 現在,讓我們使用 dumps dumps()方法將修改後的字典轉儲到新的 JSON 字符串json_str2中。
json_str2 = json.dumps(py_dict) print(json_str2) # Output {"books": [{"title": "The Wind in the Willows", "author": "Kenneth Grahame", "year": "1908"}, {"title": "To the Lighthouse", "author": "Virginia Woolf", "year": "1927"}], "movies": [{"title": "The Imitation Game", "year": "2014", "lang": "en", "watched": true}]} 正如您在上面的示例中看到的,如果沒有正確的格式,輸出 JSON 字符串很難閱讀。 您可以使用可選參數indent來添加縮進。
您可以通過將indent設置為像 2 這樣的整數來做到這一點,如下所示:
json_str2 = json.dumps(py_dict, indent = 2) print(json_str2) # Output { "books": [ { "title": "The Wind in the Willows", "author": "Kenneth Grahame", "year": "1908" }, { "title": "To the Lighthouse", "author": "Virginia Woolf", "year": "1927" } ], "movies": [ { "title": "The Imitation Game", "year": "2014", "lang": "en", "watched": true } ] }觀察輸出是如何用縮進格式化的,很容易理解。

注意:如果您希望鍵按字母順序排序,可以將
sort_keys參數設置為True。
正如您在下面的代碼片段中看到的那樣,鍵現在已按字母順序排序。
json_str2 = json.dumps(py_dict, indent = 2, sort_keys=True) print(json_str2) # Output { "books": [ { "author": "Kenneth Grahame", "title": "The Wind in the Willows", "year": "1908" }, { "author": "Virginia Woolf", "title": "To the Lighthouse", "year": "1927" } ], "movies": [ { "lang": "en", "title": "The Imitation Game", "watched": true, "year": "2014" } ] 鍵現在按字母順序顯示: "author" 、 "title"和"year" 。
到目前為止,您已經學習瞭如何在 Python 中使用 JSON 字符串。 在下一部分中,您將學習如何使用 JSON 文件。
如何在 Python 中讀取 JSON 文件
要在 Python 中讀取 JSON 文件,請使用以下語法:
json.load(<json-file>) # where <json-file> is any valid JSON file.注意我們如何使用
load()方法而不是loads()方法。loads()加載一個JSON 字符串,而load()加載一個JSON 文件。
在 Python 中處理文件時,您應該考慮使用上下文管理器。 您也可以嘗試如下讀取文件,而不使用上下文管理器:
my_file = open('students.json','r') contents = my_file.read() print(contents) file.close()如果您不關閉文件,則可能會浪費資源。
但是,在使用上下文管理器時,一旦文件操作完成,文件就會自動關閉。
並且可以使用上下文管理器來讀取文件,如下圖:
with open('students.json','r') as file: data = json.load(file) print(data) # Output {'students': [{'roll_num': 'cs27', 'name': 'Anna', 'course': 'CS'}, {'roll_num': 'ep30', 'name': 'Kate', 'course': 'PHY'}]} 當您從文件中讀取時,將模式指定為已讀——在上面的代碼中用'r'表示。
注意:為了輕鬆瀏覽當前目錄,請確保 JSON 文件與
main.py位於同一文件夾中,如下圖所示。 如果您的 JSON 文件位於不同的文件夾中,請務必指定文件的路徑。
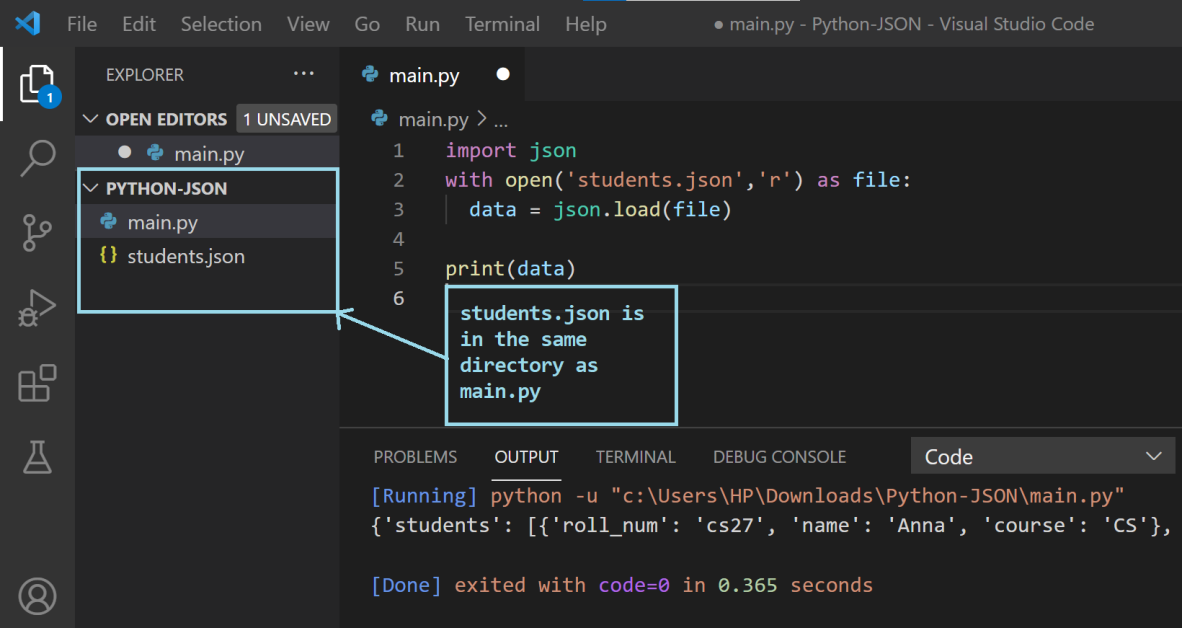
在下一部分中,您將學習如何寫入 JSON 文件。
如何在 Python 中寫入 JSON 文件
要寫入現有 JSON 文件或創建新 JSON 文件,請使用如下所示的dump()方法:
json.dump(<dict_obj>,<json_file>) # where <dict_obj> is a Python dictionary # and <json_file> is the JSON file 所以上面的語法將字典<dict_obj>轉儲到 JSON 文件<json_file>中。
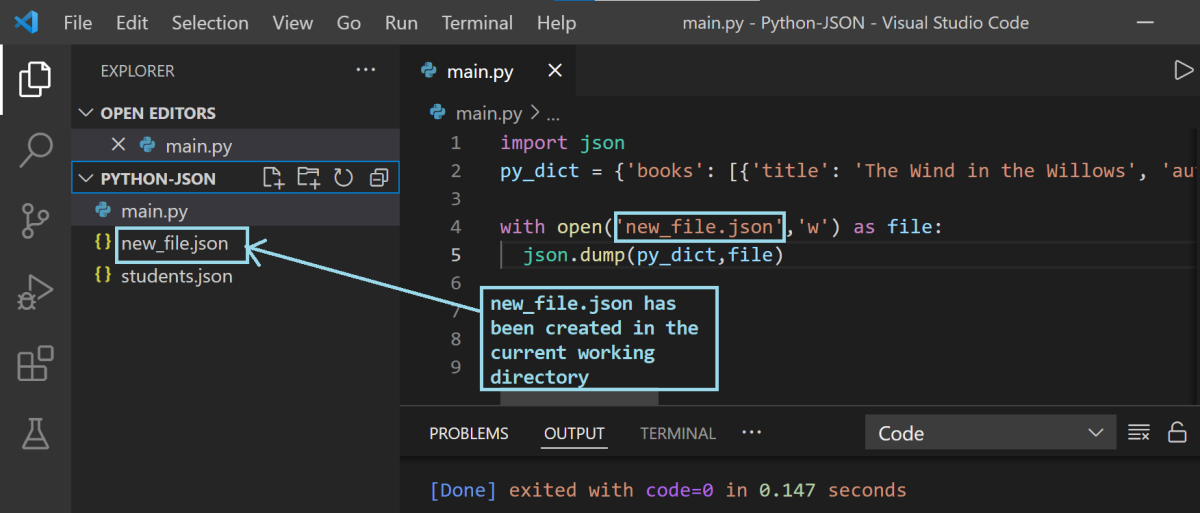
在上一節中,我們有字典py_dict 。 現在讓我們將其轉儲到一個新的 JSON 文件中。 讓我們將其命名為new_file.json 。
以下代碼單元顯示瞭如何使用dump()函數:
with open('new_file.json','w') as file: json.dump(py_dict,file)注意:如果文件存在,以寫入模式 (
w) 打開文件會覆蓋內容。 如果該文件不存在,則創建該文件。
執行上述代碼單元後,您會看到在當前工作目錄中創建了一個新的 JSON 文件。 您可以繼續檢查 JSON 文件的內容。
寫入文件時,關鍵目標是數據存儲。 如果您想保留格式,還可以使用indent和sort_keys參數。
結論
是時候快速總結一下了。
在本教程中,您學習了:
- 使用 JSON 的基礎知識,
- 如何使用
loads()和load()方法分別讀取 JSON 字符串和 JSON 文件, - 如何使用
dumps()和dump()方法將 Python 字典分別轉儲為 JSON 字符串和 JSON 文件。
我希望您發現本教程對您有所幫助。 快樂學習!
您還可以查看用於解析、格式化和驗證的 JSON 工具。
