什么是 CSS 变量以及如何使用它们
已发表: 2022-02-16在为您的站点编写 CSS 代码时,您可以利用 CSS 自定义属性(变量)来加快开发过程。 您可以使用变量来定义属性(大小、颜色),然后可以将其应用于多个元素。
这样,就可以更好地控制代码和设计。 在一个地方改变一个变量的值会覆盖在任何地方调用它的那个属性的值。
这篇文章将解释如何使用 CSS 变量和一些实际应用。
开始吧!
声明一个变量
变量可以具有全局或局部范围。 要全局定义变量,请使用 :root 选择器。
:root { --base-font-size: 1.1rem; }:root { --base-font-size: 1.1rem; }:root选择器匹配文档的根,在我们的特定情况下是<html> 。
要声明 CSS 自定义属性(变量),请从两个破折号 (--) 开始。 变量区分大小写,例如:
--base-font-size和--Base-Font-Size是两个不同的变量。
要在本地定义变量,请使用要在其中使用变量的元素的选择器。
#first-container { --background: #ccc; }#first-container { --background: #ccc; }一旦定义了变量,就需要调用它。
var() 函数
var()函数用于插入定义的 CSS 变量的值。 该函数将自身替换为变量的值。 我们来看一个例子:
HTML 代码
- 将此代码复制并粘贴到您的代码编辑器中。
- 将文件另存为index.html 。
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <link rel="stylesheet" href="/style.css"> <title>CSS Variables</title> </head> <body> <div class="wrapper"> <div class="container-1"> <p class="first">Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipisicing elit. Iste doloribus dolorum eaque veritatis quia quod?</p> <button type="button">Click here!</button> </div> <div class="container-2"> <p class="second">Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet consectetur adipisicing elit. Libero, dolorem. Reprehenderit mollitia quos quia qui.</p> <button type="button">Click here!</button> </div> <div class="container-3"> <p class="third">Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet consectetur adipisicing elit. Nisi dolor reprehenderit, ad sunt aperiam officiis!</p> <button type="button">Click here!</button> </div> </div> </body> </html><!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <link rel="stylesheet" href="/style.css"> <title>CSS Variables</title> </head> <body> <div class="wrapper"> <div class="container-1"> <p class="first">Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipisicing elit. Iste doloribus dolorum eaque veritatis quia quod?</p> <button type="button">Click here!</button> </div> <div class="container-2"> <p class="second">Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet consectetur adipisicing elit. Libero, dolorem. Reprehenderit mollitia quos quia qui.</p> <button type="button">Click here!</button> </div> <div class="container-3"> <p class="third">Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet consectetur adipisicing elit. Nisi dolor reprehenderit, ad sunt aperiam officiis!</p> <button type="button">Click here!</button> </div> </div> </body> </html>
CSS 代码
- 创建一个名为style.css的文件(在index.html的同一目录中)。
- 粘贴下面的代码并保存文件。
/* Global styles */ .wrapper, div { padding: 1rem; } div { margin: 1rem auto; } /* DEFINITION OF VARIABLES */ :root { /* Color palette */ --primary: #007bff; --success: #28a745; --warning: #ffc107; --white: #f9f9f9; --light-grey: #d8d8d8; /* Borders */ /* It is possible to use an already declared variable within the definition of another variable */ --border-primary: 1px solid var(--primary); --border-success: 1px solid var(--success); --border-warning: 1px solid var(--warning); } /* VARIABLES */ /* Wrapper */ .wrapper { background-color: var(--light-grey); } /* First Container */ .container-1 { /* The var() function replaces itself with the value of the variable */ border: var(--border-primary); color: var(--primary); background-color: var(--white); } .container-2 { /* The var() function replaces itself with the value of the variable */ border: var(--border-success); color: var(--success); background-color: var(--white); } .container-3 { /* The var() function replaces itself with the value of the variable */ border: var(--border-warning); color: var(--warning); background-color: var(--white); } .container-1 button { background-color: var(--primary); color: var(--white); } .container-2 button { background-color: var(--success); color: var(--white); } .container-3 button { background-color: var(--warning); color: var(--white); }< button {
border-radius: 5px; }/* Global styles */ .wrapper, div { padding: 1rem; } div { margin: 1rem auto; } /* DEFINITION OF VARIABLES */ :root { /* Color palette */ --primary: #007bff; --success: #28a745; --warning: #ffc107; --white: #f9f9f9; --light-grey: #d8d8d8; /* Borders */ /* It is possible to use an already declared variable within the definition of another variable */ --border-primary: 1px solid var(--primary); --border-success: 1px solid var(--success); --border-warning: 1px solid var(--warning); } /* VARIABLES */ /* Wrapper */ .wrapper { background-color: var(--light-grey); } /* First Container */ .container-1 { /* The var() function replaces itself with the value of the variable */ border: var(--border-primary); color: var(--primary); background-color: var(--white); } .container-2 { /* The var() function replaces itself with the value of the variable */ border: var(--border-success); color: var(--success); background-color: var(--white); } .container-3 { /* The var() function replaces itself with the value of the variable */ border: var(--border-warning); color: var(--warning); background-color: var(--white); } .container-1 button { background-color: var(--primary); color: var(--white); } .container-2 button { background-color: var(--success); color: var(--white); } .container-3 button { background-color: var(--warning); color: var(--white); }< button {
border-radius: 5px; } 

这里有一些注意事项:
- 创建调色板是一个简单的过程。
- 可以在另一个变量的定义中使用一个变量,例如边界变量定义中的颜色。
- 变量是继承的,.container-* 元素的颜色属性会影响其直接子元素。 在这种情况下,<p> 元素。
要覆盖变量,您可以在其容器中声明它,使其更加具体。
- 编辑CSS 代码:
button { border-radius: 5px; /* Overriding a global variable */ --primary: #021b35; }button { border-radius: 5px; /* Overriding a global variable */ --primary: #021b35; } 
变量和媒体查询
变量也可以在 CSS 媒体查询中被继承和覆盖。
- 将此代码添加到变量中:
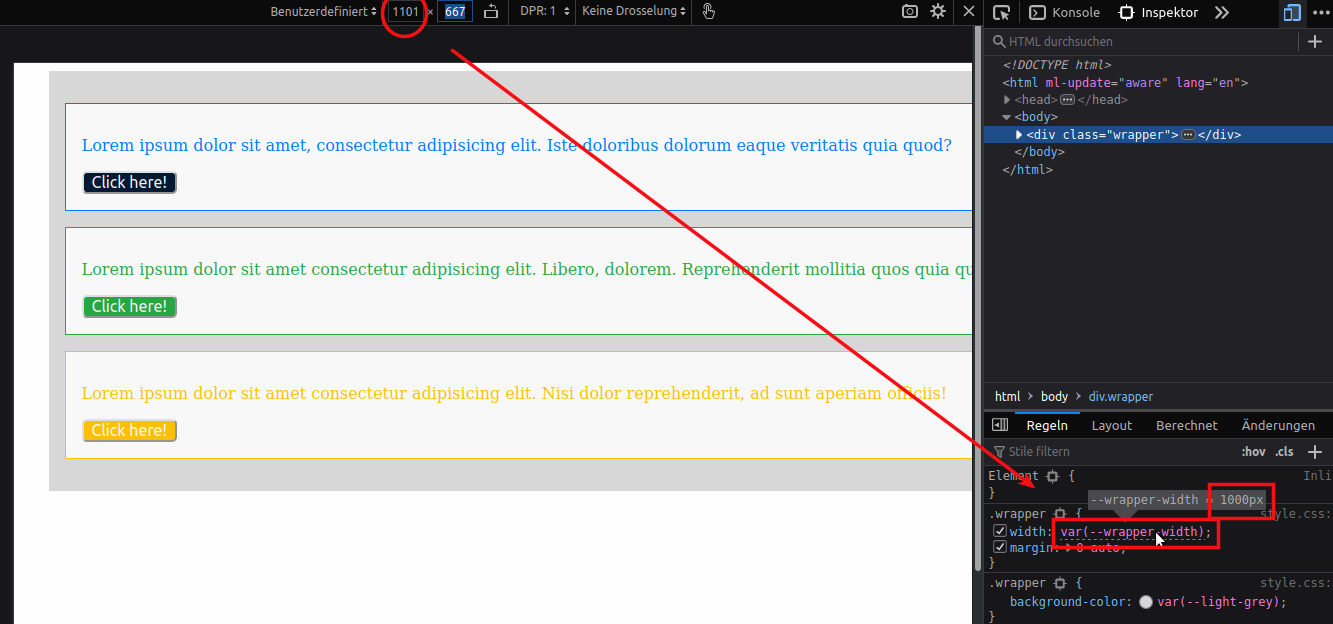
:root { /* Color palette */ --primary: #007bff; --success: #28a745; --warning: #ffc107; --white: #f9f9f9; --light-grey: #d8d8d8; /* Borders */ /* It is possible to use an already declared variable within the definition of another variable */ --border-primary: 1px solid var(--primary); --border-success: 1px solid var(--success); --border-warning: 1px solid var(--warning); /* Width of the wrapper 1000px / 90% on smaller devices */ --wrapper-width: 1000px; }:root { /* Color palette */ --primary: #007bff; --success: #28a745; --warning: #ffc107; --white: #f9f9f9; --light-grey: #d8d8d8; /* Borders */ /* It is possible to use an already declared variable within the definition of another variable */ --border-primary: 1px solid var(--primary); --border-success: 1px solid var(--success); --border-warning: 1px solid var(--warning); /* Width of the wrapper 1000px / 90% on smaller devices */ --wrapper-width: 1000px; }我们已经为包装元素定义了一个基本宽度。 我们现在可以将这些变量应用于 .wrapper 宽度属性。
- 将此代码添加到 CSS 文件的末尾:
.wrapper { width: var(--wrapper-width);
margin: 0 auto; }.wrapper { width: var(--wrapper-width);
margin: 0 auto; }
为了为屏幕宽度小于 1100 像素的设备定义媒体查询,我们编写了以下媒体查询。
- 编辑CSS 代码:
@media screen and (max-width: 1100px) { .wrapper { --wrapper-width: 90%; } }@media screen and (max-width: 1100px) { .wrapper { --wrapper-width: 90%; } }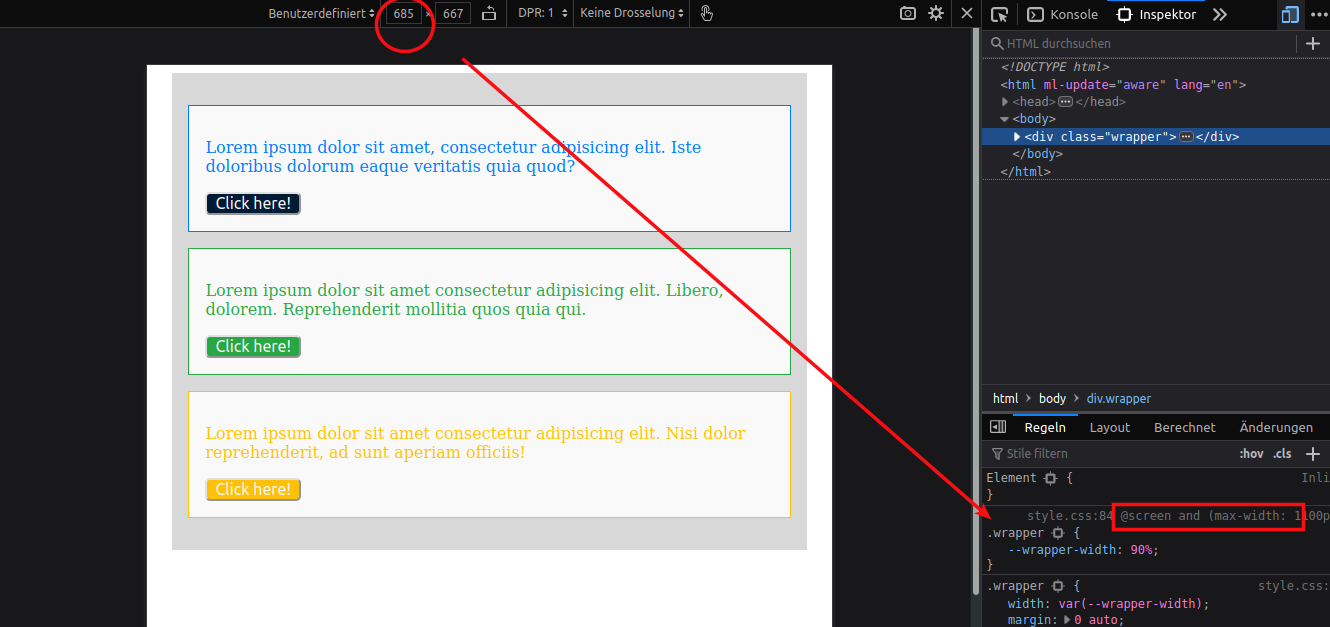
媒体查询中的新变量定义覆盖了它的值。 另请注意,该变量在 DOM 中可用,这意味着可以使用 JS 检索和操作它。 这对于 CSS 预处理器中的变量是不可能的。
概括
变量对于组织和管理少量和大量的 CSS 很有用。 它们减少了重复,从而防止了错误。 CSS 变量是动态的,这意味着它们可以在运行时更改。 使用 CSS 变量动态地为站点或应用程序设置主题很容易。 它们提供了为具有自定义名称的 CSS 属性分配值的能力。 变量遵循标准的级联规则,因此可以在不同的特异性级别定义相同的属性。
我希望你喜欢这个教程。 谢谢阅读!
